STUDY IN EUROPE
STUDY IN ASIA
‹
›
STUDY MEDICINE
OTHER PROGRAMS
STUDY IN EUROPE
STUDY IN CARIBBEAN
»
Previous
This is the last post.
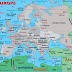
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally divided from Asia by the watershed
divides of
the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural
River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting the Black and Aegean Seas.
Europe
is bordered by the Arctic
Ocean to the north, the Atlantic
Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean
Sea to the south, and the Black Sea and connected
waterways to the southeast. Yet the borders of Europe—a concept dating back to classical antiquity—are
somewhat arbitrary, as the primarily physiographic term "continent" can incorporate cultural
and political elements.
Europe
is the world's second-smallest continent by surface area, covering about 10,180,000
square kilometres (3,930,000 sq mi) or 2% of the Earth's surface and
about 6.8% of its land area. Of Europe's approximately 50 countries, Russia is by far the largest by both area and
population, taking up 40% of the continent (although the country has territory
in both Europe and Asia), while Vatican City is the smallest. Europe is the third-most
populous continent after Asia and Africa, with a population of 739-743 million or about 11% of the world's
population. The most commonly used
currency is the euro.
Europe,
in particular Ancient
Greece and Ancient
Rome, is the birthplace of Western
culture. It played a predominant role in global
affairs from the 15th century onwards, especially after the beginning of colonialism. Between the 16th and 20th centuries,
European nations controlled at various times the Americas, most of Africa, Oceania, and the overwhelming majority of Asia. The Industrial Revolution,
which began in Great
Britain around
the end of the 18th century, gave rise to radical economic, cultural, and
social change in Western Europe, and eventually the wider world. Demographic
growth meant that, by 1900, Europe's share of the world's population was 25%.
Both world
wars were largely focused upon Europe, greatly
contributing to a decline in Western
European dominance
in world affairs by the mid-20th century as the United
States and Soviet
Union took prominence. During the Cold
War, Europe was divided along the Iron
Curtain between NATO in the west and the Warsaw Pact in the east. European integration led to the formation of the Council of Europe and the European Union in Western Europe, both of which have been
expanding eastward since the revolutions of 1989 and
the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991. The European Union nowadays has
growing influence over its member countries. Many European countries are
members of the Schengen Area, which abolishes border and immigration controls
among its members.
Climate
Europe
lies mainly in the temperate climate zones, being
subjected to prevailing westerlies.
The
climate is milder in comparison to other areas of the same latitude around the
globe due to the influence of the Gulf Stream. The Gulf Stream is nicknamed "Europe's central heating", because it makes
Europe's climate warmer and wetter than it would otherwise be. The Gulf Stream
not only carries warm water to Europe's coast but also warms up the prevailing
westerly winds that blow across the continent from the Atlantic Ocean.
Therefore the average temperature
throughout the year of Naples is 16 °C (60.8 °F), while it is only
12 °C (53.6 °F) in New York City which is almost on the same
latitude. Berlin, Germany; Calgary, Canada; and Irkutsk, in the Asian part of
Russia, lie on around the same latitude; January temperatures in Berlin average
around 8 °C (15 °F) higher than those in Calgary, and they are almost
22 °C (40 °F) higher than average temperatures in Irkutsk
Language
European languages
mostly fall within three Indo-European language groups: the Romance
languages, derived from the Latin of the Roman
Empire; the Germanic languages, whose ancestor
language came from southern Scandinavia; and the Slavic
languages.
Slavic languages
are most spoken by the number of native speakers in Europe; they are spoken in
Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Romance languages are spoken
primarily in south-western Europe as well as in Romania and Moldova, in Central or
Eastern Europe. Germanic languages are spoken in Northern Europe, the British
Isles and some parts of Central Europe.
Many other
languages outside the three main groups exist in Europe. Other Indo-European
languages include the Baltic group (that is, Latvian and Lithuanian), the Celtic group (that is, Irish, Scottish Gaelic, Manx, Welsh, Cornish, and Breton), Greek, Armenian, and Albanian. In addition, a distinct group of Uralic
languages (Estonian, Finnish, and Hungarian) is spoken mainly
in Estonia, Finland, and Hungary, while Kartvelian languages (Georgian, Mingrelian, and Svan), are spoken primarily in Georgia, and two other language families reside in the North Caucasus
(termed Northeast Caucasian, most notably
including Chechen, Avar and Lezgin and Northwest Caucasian, notably
including Adyghe). Maltese is the only Semitic
language that is official within
the EU, while Basque is the only European language isolate. Turkic languages include Azerbaijani and Turkish, in addition to the languages of minority nations in Russia.
Multilingualism
and the protection of regional and minority languages are recognised political
goals in Europe today. The Council of Europe Framework Convention for the
Protection of National Minorities and the
Council of Europe's European Charter for Regional
or Minority Languages set up a legal framework
for language rights in Europe.
Countries
Countries in
Europe are presented below in different groups and associations they
belong.
Tagged with: STUDY IN EUROPE
About Higherwayedu
Higherway Educational Consultant is an educational consultant that provides admission services for students wishing to study abroad.
»
Previous
This is the last post.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)









Your write-ups are far more than wow!
ReplyDeleteYour Domain Name
Europe is good for travelling.
ReplyDeleteThe fastest method to make your outing however costly as conceivable may be to limit your hunt to something amazingly explicit. Europa-Road túlméretes szállítás
ReplyDelete